Checking the oil level
Check the engine oil level at each fuel stop.
1. Park the vehicle on a level surface and stop the engine.
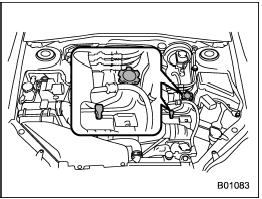
Turbo models
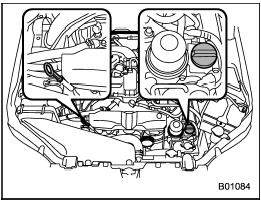
Non-turbo models
2. Pull out the level gauge, wipe it clean, and insert it again.
3. Be sure the level gauge is correctly inserted until it stops.
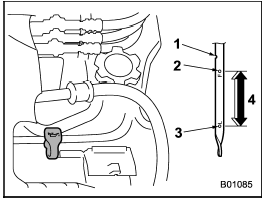
Turbo models
1) Notch
2) Upper level
3) Lower level
4) Approximately 1.1 US qt (1.0 liter, 0.9
Imp qt) from lower level to upper level
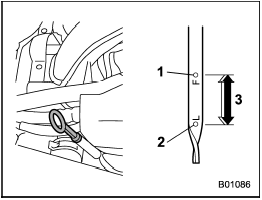
Non-turbo models
1) Upper level
2) Lower level
3) Approximately 1.1 US qt (1.0 liter, 0.9
Imp qt) from lower level to upper level
4. Pull out the level gauge again and check the oil level on it. If it is below the lower level, add oil to bring the level up to the upper level.

- Use only engine oil with the recommended grade and viscosity.
- Be careful not to spill engine oil when adding it. If oil touches the exhaust pipe, it may cause a bad smell, smoke, and/or a fire. If engine oil gets on the exhaust pipe, be sure to wipe it off.
If you check the oil level just after stopping the engine, wait a few minutes for the oil to drain back into the oil pan before checking the level.
Just after driving or while the engine is warm, the engine oil level reading may be in a range between the upper level and the notch mark. This is caused by thermal expansion of the engine oil.
To prevent overfilling the engine oil, do not add any additional oil above the upper level when the engine is cold.
See also:
Under-floor storage compartment
The subfloor storage compartment is located under the floor of the trunk or cargo
area and can be used to store small items. To open the lid, pull the tab or handle
up.
NOTE
When storing a flat ...
Programming the transmitters
The remote keyless entry system is equipped with a special code learning feature
that allows you to program new transmitter codes into the system or to delete old
ones. The system can learn up to ...
Light control and wiper control levers/switches
1) Windshield wiper
2) Mist
3) Windshield washer
4) Rear window wiper and washer switch
5) Wiper intermittent time control switch
6) Wiper control lever
7) Light control switch
8) Fog light s ...


